Rotating Unions and Rotary Joints (also known as rotary swivels, rotary couplings) are precision mechanical devices used to transfer fluid from a stationary source, such as a supply pipe, into a rotating piece of machinery. Rotating Unions and Rotary Joints are used in numerous manufacturing processes to cool, heat, or transfer fluid (pneumatic or hydraulic) power.
Industries
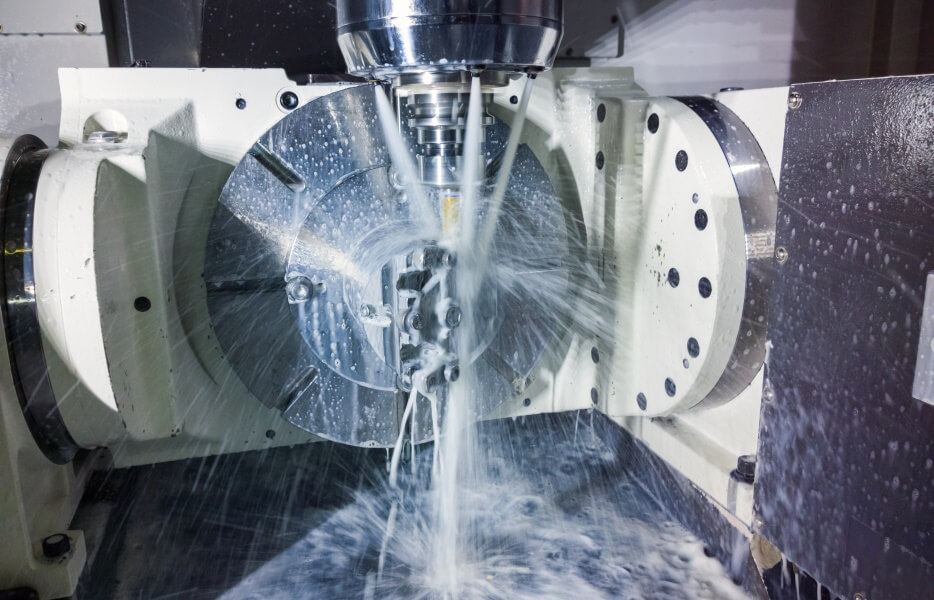
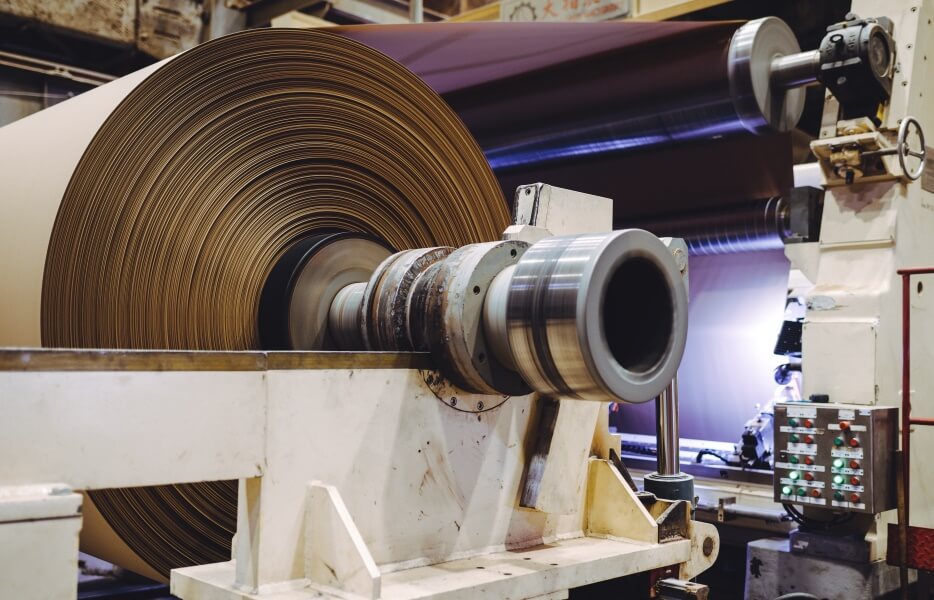
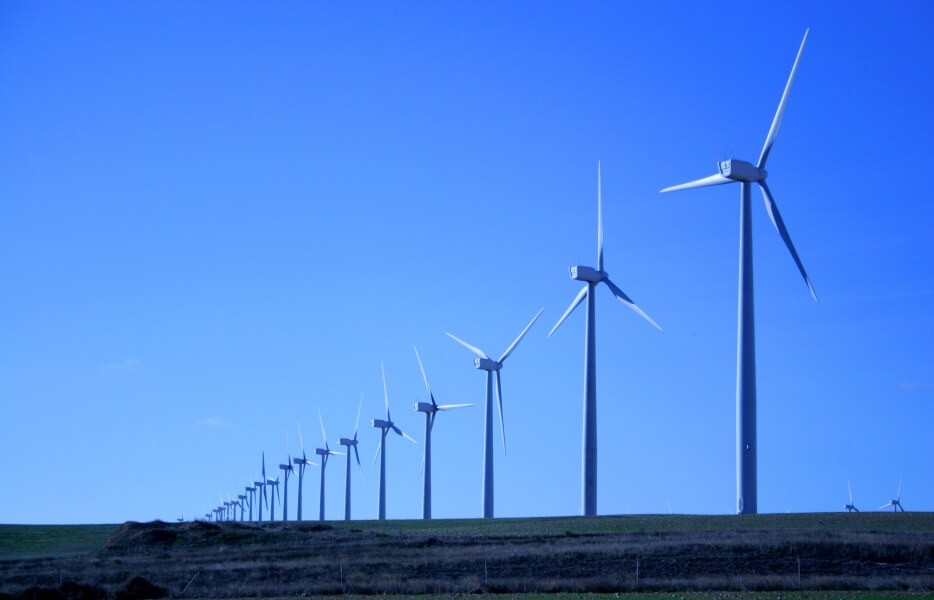
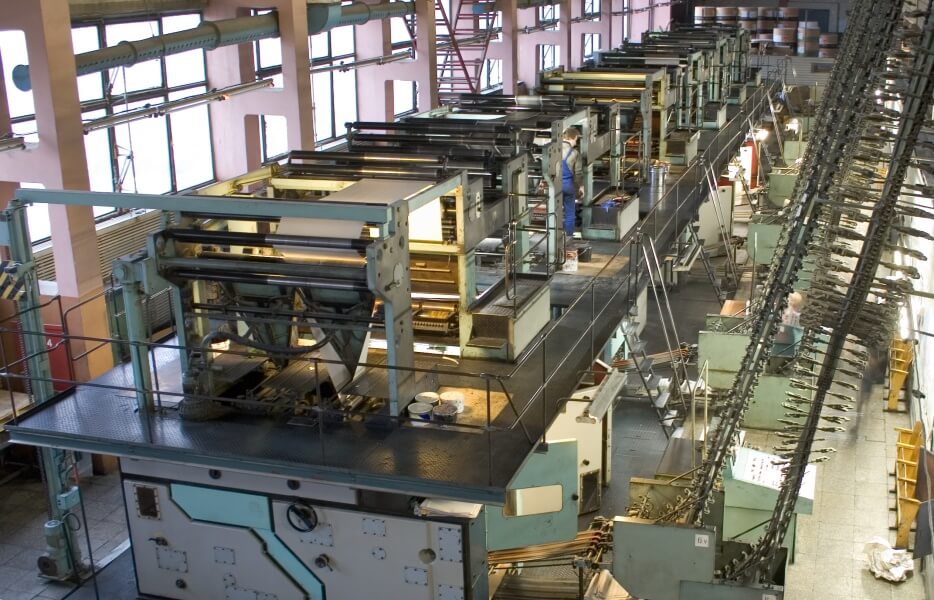
Deublin rotary unions and electrical slip rings are used by all kinds of industrial machinery and manufacturing processes.
Machine Tool | Paper & Corrugating |
Renewable Energy | Printing & Packaging |
Oil & Gas | Metals Processing |
Semiconductor | Agriculture & Construction |
Proper selection of a Rotating Union requires detailed:
Equipment Fitting Information:
Union Size & Thread Spec:
- This is the nominal size of the union and the thread or attachment specification of the Rotating Union for installation on to the machine roll.
- Example: 1” NPT RH, 5/8-18 UNF LH, 2” BSP LH, etc
Number of Passages
- Union may have 1, 2, 3, 4 or more passages. If there are 2 passages, the Union may be Duoflow where the same media enters and exits through the same union. Alternatively, 2 passages could transmit the same media at two different pressures or 2 separate media could be transmitted at 2 different pressures.
Supply Pipe:
- Most Duoflow unions allow fluid to flow in and out through the same union. This type of closed circuit flow requires a supply pipe to either deliver or serve as a channel for the media to return. Supply/Return pipes are supported at one end by the union and the other end might simply be cantilevered into the roll or may be supported by some sort of a bushing or spider. Supply/Return Pipes, depending on the roll configuration of the machine, may by stationary or rotating.
Operating Parameters:
Media
- What is the media being transmitted? It may be water, air, hydraulic fluid, coolant, steam, hot oil, etc
Pressure
- An application may require transmittal of a single media at a single pressure. Sometimes, the pressure may vary. Always consider the max operating pressure as the operating pressure. Also, if the application calls for multi passages, it is important to know the max pressure of each media and the channel (inner or outer) being considered for flow of respective media.
Temperature
- For most water applications, the media temperature might be ambient. However, it is important to know the temperature of the media. Rotating Unions comprise of various internal components with their individual temperature limits. Rotating Unions with standard deep groove ball bearings have a temperature limit of 250F/120C. Heat stabilized bearings with special hi-temp grease extend the temperature to 320F/160C. For higher temperatures yet, bushing type bearings are utilized since they are self- lubricating and typically have much higher temperature limits.
Speed & direction of Rotation
- This is a critical Operating Parameter. Higher speeds machine require better alignment of Rotating Union to the machine roll. NPT threads are quite suitable for slower machine speeds. Beyond 1500 rpm, NPT threads, due to the taper, do not provide accurate alignment of the Rotating Union relative to the machine roll. In these instances, machine thread is recommended. For higher speeds yet, such as machine tool applications, the Rotor of the Rotating Union features a ground cylindrical pilot surface for accurate installation and alignment.
- Direction of Rotation is an equally critical Parameter. High speed machine tool spindles accelerate at a very rapid speed. The thread direction must always be opposite to the direction of rotation of the spindle. For slow speed applications, this may not be so critical. However, in order to fit any rotating union, the thread direction must be consistent with the direction of threads of the roll.